Create Your First Cluster
This guide will help you set up your first Edka Kubernetes cluster.
Prerequisites
- A Hetzner Cloud account. If you don’t have one, see our Prerequisites page for detailed instructions.
- A Hetzner Cloud API token with read/write permissions. Check our Prerequisites page for detailed instructions.
Optional:
- Kubectl (Kubernetes CLI - only necessary for advanced operations)
- Lens - a Kubernetes IDE (recommended for managing advanced operations with your cluster visually)
If you don’t have these yet, see our Prerequisites page for detailed instructions.
Note: Kubernetes knowledge is not required to use Edka, but it can be helpful for advanced operations.
Step 1: Create an Edka Account
- Go to console.edka.io and click Create Account
- Sign up using your email or Google account
- Verify your email address
Step 2: Prepare Your Hetzner Token
- Generate a Hetzner API token with read/write permissions (see prerequisites)
- Decide how you want to use it:
- Store a token per cluster (recommended)
- Use a temporary token during creation (not stored)
- Use the account-level integration (legacy). Useful for quickly creating a cluster without always having to provide a token.
Edka uses a unique token per cluster (recommended). You can add or update the token later in Clusters > your cluster > Settings > General. After the cluster is created, only the cluster owner and organization owners/admins can update or remove the stored cluster token.
Note: The account-level integration in Settings > Integrations > Hetzner (Legacy) is reccomended for testing and development purposes.
Step 3: Create Your First Cluster
- In the Edka dashboard, navigate to Clusters
- Choose a name for your cluster (e.g., “clusterone”)
- Click Create Cluster
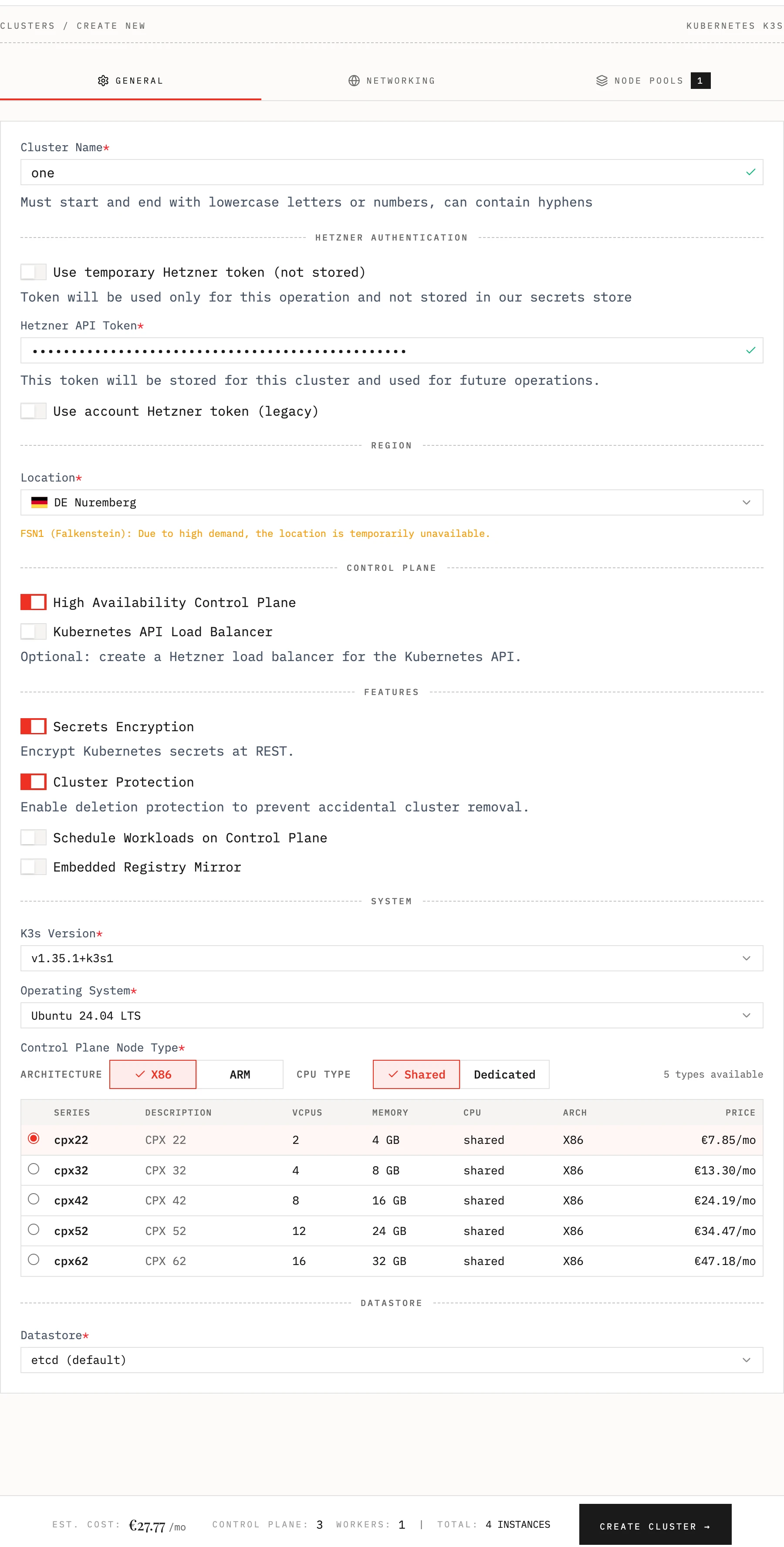
Optional settings:
-
Cluster location (e.g. Nuremberg)
-
Kubernetes version (e.g., 1.35.1-k3s1)
-
Instance type for control plane and node pools (e.g., CX23)
-
Set a highly available control plane (recommended for production)
-
Use a Load Balancer in front of your Kubernetes API
-
Encrypt Kubernetes secrets at REST
-
Enable deletion protection to prevent accidental cluster removal
-
Schedule Workloads on Control Plane
-
Embedded Registry Mirror
-
Choosing the Operating System. Currently supported:
- Ubuntu 24.04
- Debian 13 (Trixie)
- Rocky Linux 10
- Fedora 43
- Alma Linux 10
-
Use an external datastore, like MySQL or Postgres to store cluster state
e.g. postgres://username:password@hostname:port/database-name
-
Customize the network settings in the Network tab
-
Chose between Flannel or Cilium CNI and enable CNI Encryption
-
Restrict the access to instances SSH and Kubernetes API to your own IPs
-
For cluster larger than 100 instances you have to use Host Firewall (Cilium). This enables Cilium host firewall and forces public networking with Cilium encryption
-
Set the Private Network Subnet
-
Choose the number of instances and node pools in the Node Pools tab
-
Set extra node label and taints. Taints can only be configured on additional node pools
-
Provide a cluster token (stored per cluster), use a temporary token (not stored) or use a token stored per account
Edka will provision your Kubernetes cluster in about 2 minutes. You’ll see the progress and events as the process completes.
Cluster events are always accessible in the Cluster Events tab.
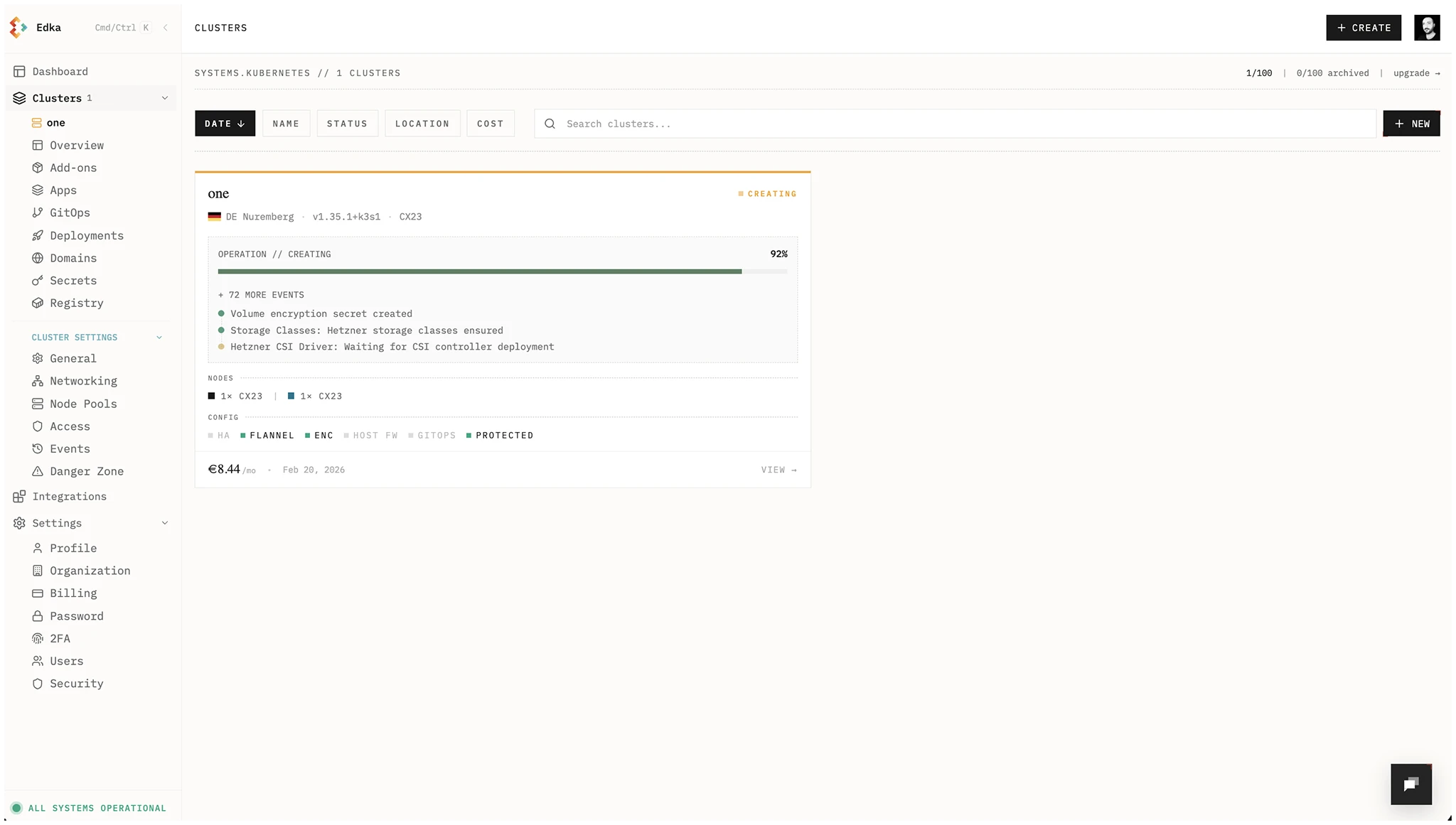
Step 4: Access Your Cluster
- In the Clusters dashboard, open your cluster Overview or go to Settings > Access & Security
- Under Kubeconfig, click Download Kubeconfig. Each user gets their own kubeconfig and downloads are audited.
- If you need a new kubeconfig, use Rotate Credentials in Access & Security to invalidate the old one and download a fresh version. If your access is revoked, contact the account owner.
Set the KUBECONFIG environment variable to point to the downloaded file:
Admin note: Owners and admins can manage team kubeconfigs in Settings > Access & Security under Team Access. Use Rotate to invalidate a user’s kubeconfig or Revoke to remove access.
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/your/kubeconfig.yamlVerify the connection to your cluster:
kubectl get nodesYou should see a list of nodes in your cluster:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSIONone-master1 Ready control-plane,etcd,master 2m30s v1.35.1-k3s1one-pool-default-worker1 Ready worker 1m45s v1.35.1-k3s1one-pool-default-worker2 Ready worker 1m45s v1.35.1-k3s1Alternatively, you can use Lens to manage your cluster visually. Just add the kubeconfig file to Lens and connect to your cluster.
Next Steps
Now that you have your first cluster running, let’s set up some add-ons to transform it into a performant and production ready platform: